ref
在 React 中,Ref 主要用于下面两个用途:
- 引用 DOM 节点
- 函数组件中的“实例变量”
本篇文章将会阐述这两个常见用法。
DOM Refs
此章节对应的是 Ref 的第一个用途,即“引用 DOM 节点”,我们称之为DOM Refs。
Refs 提供了一种方式,允许我们访问 DOM 节点或在 render 方法中创建的 React 元素。
在典型的 React 数据流中,props是父组件与子组件交互的唯一方式。要修改一个子组件,你需要使用新的 props 来重新渲染它。但是,在某些情况下,你需要在典型数据流之外强制修改子组件。被修改的子组件可能是一个 React 组件的实例,也可能是一个 DOM 元素。对于这两种情况,React 都提供了解决办法。
何时使用 Refs
下面是几个适合使用 refs 的情况:
- 管理焦点、文本选择或媒体播放。
- 触发强制动画。
- 集成第三方 DOM 库。
避免使用 refs 来做任何可以通过声明式实现来完成的事情。举个例子,避免在Dialog组件里暴露open()和close()方法,最好传递isOpen属性。
创建 refs
在函数组件中,使用useRef创建 refs,并可以通过ref属性附加到 React 元素。
import React, { useRef } from 'react';
function MyComponent() {
const myRef = useRef();
return <div ref={myRef} />;
}
在类组件中,使用React.createRef()创建 refs,并可以通过ref属性附加到 React 元素。我们通常将 refs 分配给实例属性。
class MyComponent extends React.Component {
constructor(props) {
super(props);
this.myRef = React.createRef();
}
render() {
return <div ref={this.myRef} />;
}
}
访问 refs
ref是一个有current属性的对象,current属性就是被引用的节点。
函数组件中:
const node = myRef.current;
类组件中:
const node = this.myRef.current;
ref 的值根据节点的类型而有所不同:
- 当
ref属性用于 HTML 元素时,通过useRef或者createRef创建的ref接收底层 DOM 元素作为其current属性。 - 当
ref属性用于自定义 class 组件时,ref对象接收组件的挂载实例作为其current属性。 - 你不能在函数组件上使用
ref属性,因为它们没有实例。
为 DOM 元素添加 ref
函数组件:
import React, { useRef } from 'react';
function CumstomTextInput() {
const textInputRef = useRef<HTMLInputElement>();
const focusTextInput = () => {
if (textInputRef.current) {
textInputRef.current.focus();
}
};
return (
<div>
<input type="text" ref={textInputRef} />
<button onClick={focusTextInput}>Focus the text input</button>
</div>
);
}
类组件:
class CustomTextInput extends React.Component {
constructor(props) {
super(props);
// 创建一个 ref 来存储 textInput 的 DOM 元素
this.textInput = React.createRef();
this.focusTextInput = this.focusTextInput.bind(this);
}
focusTextInput() {
// 直接使用原生 API 使 text 输入框获得焦点
// 注意:我们通过 "current" 来访问 DOM 节点
this.textInput.current.focus();
}
render() {
// 告诉 React 我们想把 <input> ref 关联到
// 构造器里创建的 `textInput` 上
return (
<div>
<input type="text" ref={this.textInput} />
<input
type="button"
value="Focus the text input"
onClick={this.focusTextInput}
/>
</div>
);
}
}
React 会在组件挂载时给current属性传入 DOM 元素,并在组件卸载时传入null值。ref会在useEffect、componentDidMount、componentDidUpdate触发之前更新。
为 class 组件添加 ref
如果我们想包装上面的CustomTextInput(类组件),来模拟它挂载之后立即被点击的操作,我们可以使用 ref 来获取这个自定义的 input 组件并手动调用它的focusTextInput方法:
class AutoFocusTextInput extends React.Component {
constructor(props) {
super(props);
this.textInput = React.createRef<CustomTextInput>();
}
componentDidMount() {
this.textInput.current.focusTextInput();
}
render() {
return <CustomTextInput ref={this.textInput} />;
}
}
请注意:CustomTextInput是类组件时,上面的代码才有效!
将 DOM Refs 暴露给父组件
在极少数情况下,你可能希望在父组件中引用子节点的 DOM 节点。通常不建议这样做,因为它会打破组件的封装,但它偶尔可用于触发焦点或测量子 DOM 节点的大小或位置。
虽然你可以向子组件添加 ref,但这不是一个理想的解决方案,因为你只能获取组件实例而不是 DOM 节点。并且,它还在函数组件上无效。
有以下几种方式:
- Ref 转发:Ref 转发使组件可以像暴露自己的 ref 一样暴露子组件的 ref。
- 使用其他的属性名传递
ref,如 styled-components 旧版本通过innerRef属性接收ref。 - 使用findDOMNode()获取子组件的 DOM 元素。 —— 警告:不要再使用这个 API,即将被废弃。
这里重点说一下 Ref 转发。
上文我们在AutoFocusTextInput时,只处理了 class 组件的版本,如果是函数组件,可以通过 ref 转发来实现。
CustomTextInput组件:
import React, { useRef } from 'react';
const CumstomTextInput = React.forwardRef(function(props, ref) {
return (
<div>
<input type="text" ref={ref} />
</div>
);
});
CustomTextInput.displayName = 'CustomTextInput';
export default CustomTextInput;
AutoFocusTextInput组件:
import React, { useRef } from 'react';
import './CustomTextInput';
function AutoFocusTextInput() {
const textInputRef = useRef();
useEffect(() => {
if (textInputRef.current) {
textInputRef.current.focus();
}
}, []);
return <CustomTextInput ref={textInputRef} />;
}
重点:
- React.forward() 会创建一个 React 组件,这个组件能够将其接收的 ref 属性转发到其组件树下的另一个组件中。
CustomTextInput.displayName = 'CustomTextInput';是为了在调试工具中显示正确的组件名,方便调试。
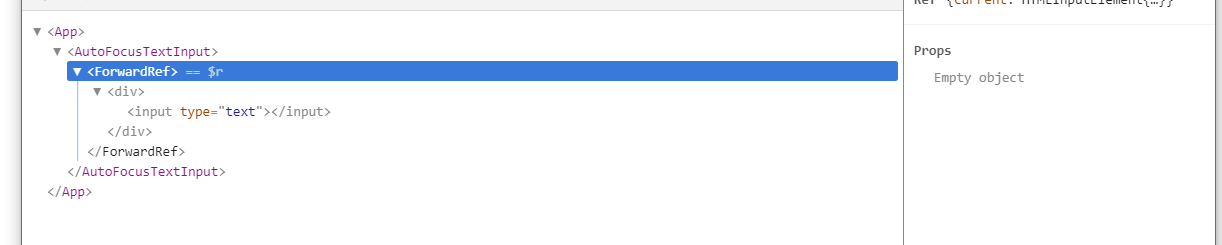
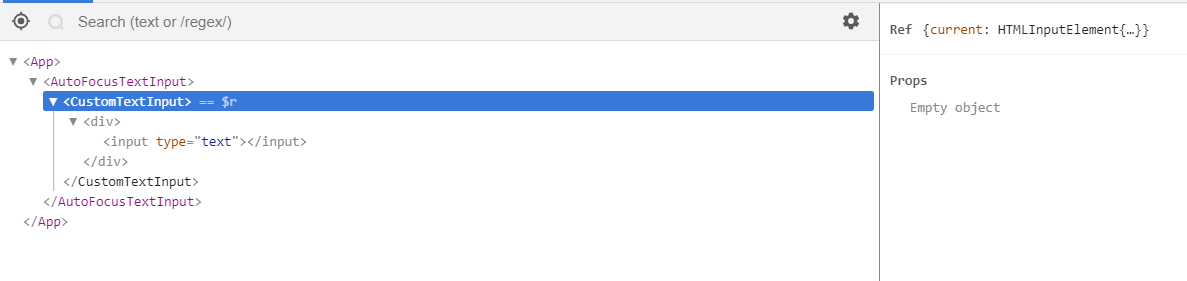
可以看一下去掉CustomTextInput.displayName = 'CustomTextInput';前后的 React Devtools 展现的元素树结构:
去掉后:
加上后:
函数组件中的“实例变量”
在函数组件中,我们可以使用useRef()创建一个ref对象。不管这个函数组件重绘了多少次,useRef()返回的总是第一次渲染此函数组件时创建的ref对象。而且ref对象的current属性可以存放任何 js 数据,所以,我们可以借助useRef()创建的ref对象实现类似 class 的“实例变量”。
如下面的例子:
function Timer() {
const intervalRef = useRef();
useEffect(() => {
const id = setInterval(() => {
// ...
});
intervalRef.current = id;
return () => {
clearInterval(intervalRef.current);
};
});
// ...
}